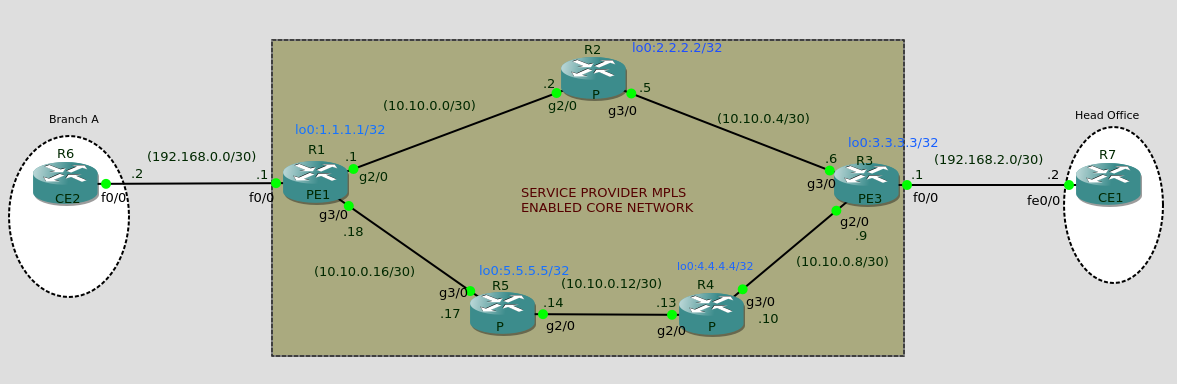
MPLS-VPN
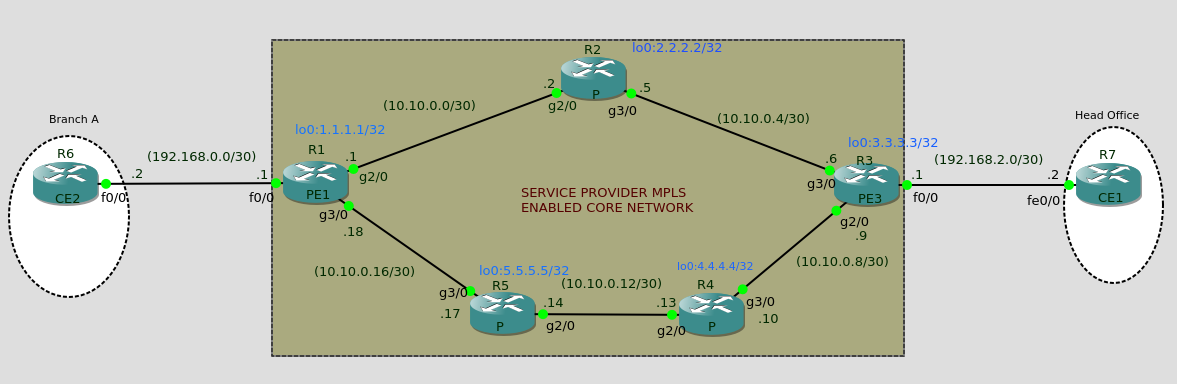
L3MPLS VPN Definitions: VRF – Virtual Routing Instance. Its an Instance of a routing table – Each customer has their own VRF defined with different definitions of RD and RT Route Distinguisher (RD); Used to uniquely identify routes belonging to a particular VRF. Route Targets (RT); Used to specify how routes are imported and exported from VRF. MP-BGP; Multiprotocol BGP- Used to carry BGP routes and VPN routes between PE Routers. Setup: Required; VPN to interconnect Head office to a branch office. 1. Define VRF, RD and RT VRF = Trust-Bank Route Distinguisher (RD): 37027:20 Route Targets (RT): 37027:20 PE1(config)#ip vrf Trust-Bank PE1(config-vrf)#rd 37027:20 PE1(config-vrf)#route-target both 37027:20 2. Enable VRF on the client facing interface on the PE routers and assign IP to be used to communicate to CE VRF = Trust-Bank R1(config)# int fastEthernet 0/0 R1(config-if)# ip vrf forwarding Trust-Bank R1(config-if)# ip add 192.168.2.1 255.255...